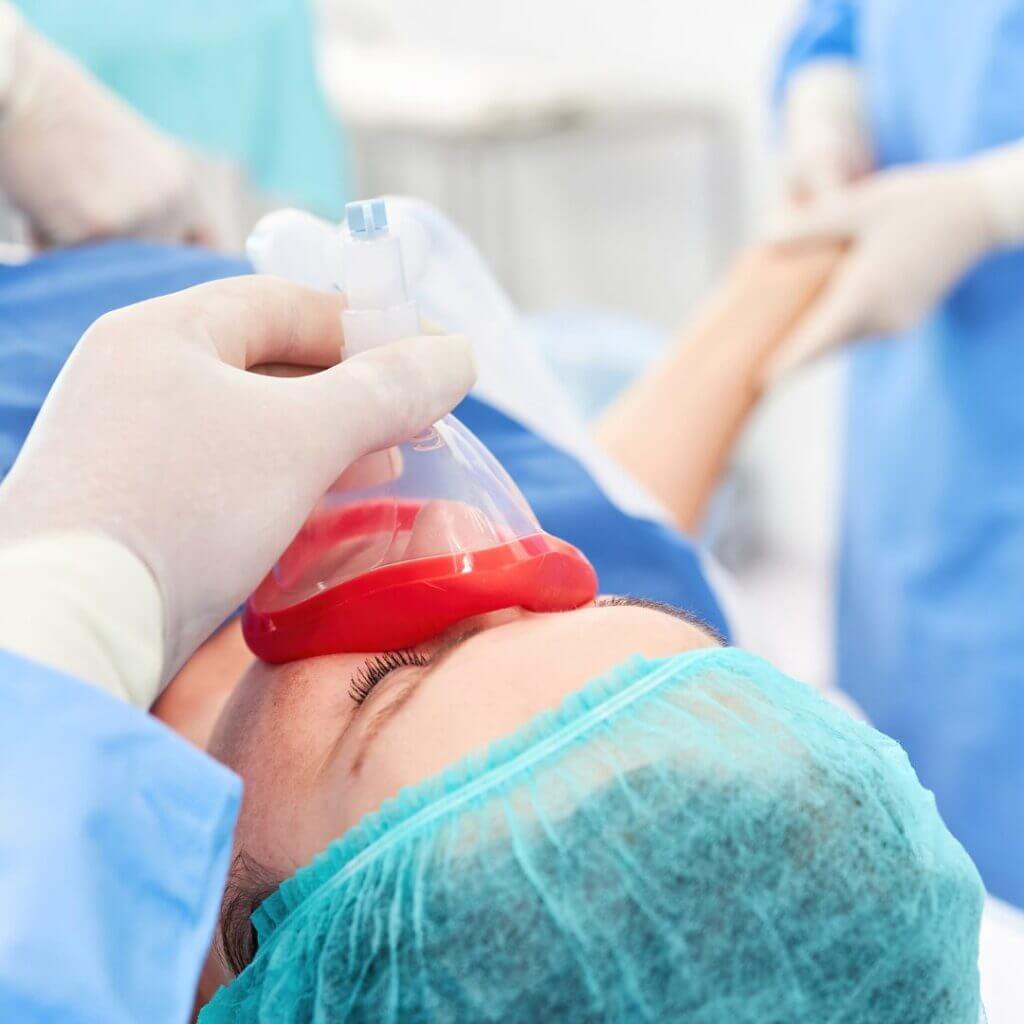
Medical students take many exams and certifications, yet at what point do they decide on their career? The career path for physicians can vary greatly. Locum tenens providers have a large variety of specialties. People who want to work in surgeries but don’t want to be a surgeon can choose a career in anesthesiology.
What is the scope of practice for anesthesiologists?
Anesthesiologists, who specialize in anesthesia, primarily monitor patients before, during, and after using anesthesia. This happens mostly for surgical procedures, so they work with surgeons regularly. Their role can involve using general anesthesia, regional anesthesia, and local anesthetics. They are well versed in all types of anesthesia.
They can also help manage pain relief, or deal with chronic pain, by using nerve blocks and pain medicine. Anesthesiologists can be both MDs and DOs. For their practice, anesthesiologists can supervise Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs), and practice independently.
How do I become an anesthesiologist?
Anesthesiologists follow the same procedure as other physicians. They earn a bachelor’s degree with an appropriate major from an undergraduate institution. The next step would be to take the MCAT and attend four years of medical school.
They must then pass a national board exam — either the USLME or COMLEX — and complete at least two years of residency. Students attending MD-granting medical schools take the USMLE, while osteopathic medical students take the COMLEX. The USMLE focuses on allopathic medicine, while the COMLEX focuses on osteopathic principles.
Doctors must finish either national exam and then complete residency programs. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), the American Osteopathic Association (AOA), or Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada (RCPSC) must approve the programs. Hospitals and other employers are increasingly requiring anesthesiologists to be board certified. You can do this through the American Board of Anesthesiology (ABA), the American Board of Physician Specialties (ABPS), and the American Osteopathic Board of Anesthesiology (AOBA).
How long does it take to become an anesthesiologist?
Generally it takes about 10 to 12 years to become an anesthesiologist. This includes the four years to earn an undergraduate degree, four years of medical school, and two to four years of residency. Earning a license as an anesthesiologist does not have a simple shortcut. As with all physician careers, it takes many years and dedication.
What exams do anesthesiologists need to take?
Anesthesiologists take the same exams as other physicians, along with the required exams by the certifying bodies. The Board of Certification in Anesthesiology (BCA) within the ABPS offers this. Their exam has two parts: a written test with 200 multiple-choice questions lasting four hours, and an oral exam.
The written portion dives into seven domains: pharmacology, anesthetic management, anesthetic preparation, anatomy preparation, anatomy and physiology, diseases, anesthesia subspecialties, and perioperative complications. They split their exam into two segments: a 200-multiple choice written exam and an oral exam.
Another organization that anesthesiologists can receive certification from is the ABA, who offers three exams for physicians. The first is the Advanced Exam which focuses on the clinical aspects of anesthetic practice. The Applied Exam contains a Standardized Oral Examination (SOE) and the Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE).The last are the Subspecialty Exams, which anesthesiologists can use to certify themselves in specific areas. Some of these areas are critical care medicine, pediatric anesthesiology, and neurocritical care. Each one may have different eligibility requirements.
What licenses do anesthesiologists need?
Physicians must obtain a license and certification from the ABA, ABPS, or AOBA to practice anesthesiology. State laws typically regulate the licensing of anesthesiology assistants or CRNAs. But there may be specific licensing requirements for anesthesiologists.
What are the continuing education requirements for anesthesiologists?
Both the ABA and ABPS offer the Continuing Medical Education (CME) requirements for anesthesiologists. Anesthesiologists need to earn 125 CME credits in 5 years and another 100 in 10 years for ABA recertification. Anesthesiologists earn 250 CME credits in 10 years, with 20 credits focused on ABA-approved patient safety.
To maintain certification by the ABPS, you must complete 50 Category 1 CME hours each year. At least 25 of those hours must be in anesthesiology. The anesthesiologist should complete 400 CME hours over eight years, with 200 hours focused on anesthesiology topics.
They must also complete 50 self-assessment CME questions each year, besides the final year. To complete the process, you need to earn four CME credits from AAPS-approved courses.
How much do anesthesiologists make?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, anesthesiologists earn around $339,000 annually as of May 2023. They also report that Connecticut is the top-paying state for anesthesiologists at around $360,000 annually. For more on anesthesiologist salaries, check out our anesthesiologist salary guide.
Are you an anesthesiologist looking for a job? Check out our job board to see available positions all over the United States.
This article was written by Desirae Sin
